Enterprise Content Management in Microsoft 365: A complete guide
Table of contents
Enterprise Content Management (ECM) in Microsoft 365 provides a set of processes, methods, and tools designed for complete content lifecycle management. It saves time and resources, ensures regulatory compliance, cuts unnecessary costs, improves content accessibility and customer satisfaction, and supports business continuity.
Benefits of Microsoft ECM:
- Centralized management: Streamlines content management by centralizing documents and information.
- Enhanced collaboration: Facilitates collaboration through seamless integration with Microsoft 365 apps.
- Improved compliance: Helps organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements.
- Scalability and flexibility: Adapts to the changing needs of the organization with scalable cloud infrastructure.
- Cost efficiency: Reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure and maintenance.
Why is the Microsoft 365 ECM important?
The total amount of data created and consumed globally reached 79 zettabytes in 2021. The number is projected to grow to 181 zettabytes by 2025.
That’s a LOT of data.
However, out of all the data created for business purposes, only a small percentage will get stored, and an even smaller percentage will be managed properly.
This is where enterprise content management comes in.
Content management lifecycle in Microsoft 365
The modern approach to ECM reflects the ways in which users create and consume content.
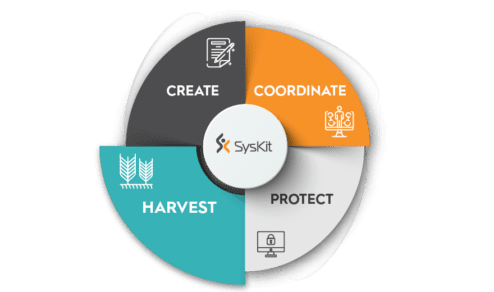
Rather than becoming dormant, Microsoft 365 ECM tools and capabilities enable content to gain value over time while retaining control of the management process. They consequently contribute to each of the four stages of content lifecycle management: Create, Coordinate, Protect, and Harvest (see graph below).
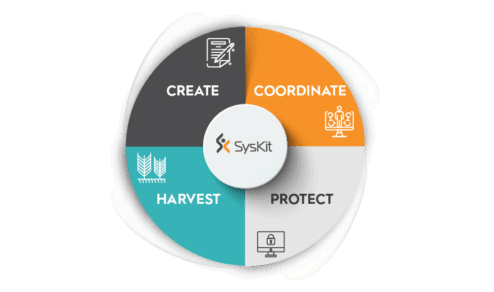
This article will guide you through the most useful Microsoft 365 ECM features, tools, and capabilities for your corporation, and serve you as a starting point for their implementation. Let’s dive in!
Create
SharePoint Online vs. OneDrive – What is the difference?
Microsoft 365 incorporates a series of different tools for storing, accessing, and managing a variety of documents used in your everyday work. When choosing the right cloud-based storage solution, your choice will depend on your business needs. What is the difference between OneDrive and SharePoint, for instance?
SharePoint Online is a collaborative, cloud-based platform that functions as a single knowledge base of valid and authorized information. It powers content collaboration across M365, including files you work with in Teams, Yammer, and Outlook. It enables portals, news, pages, lists, and a platform for business apps. OneDrive, on the other hand, allows you to store your private files in a centralized location, and access them from a variety of devices. As soon as you’re ready to share your files, you can easily do that. In OneDrive, you’re the owner of the created documents, whereas in SharePoint the content ownership belongs to the site owner.
Regardless of the one you choose, both options surpass the document level and go further to enable content creation and collaboration. Microsoft Teams is another collaboration hub that comes into play here. To find out more about how it differs from SharePoint, make sure to read our SharePoint vs Teams blog post.
Coordinate
Document management in Microsoft 365
A study by Nucleus Research found that as much as $9.8 million annually can be saved through the proper use of a content services system. Most time gets wasted searching for the existing documents and re-creating new ones.
Time, it turns out, really is money.
Document management in Microsoft 365 can help you save both using the following capabilities:
- Mentioning a user in a OneDrive comment to attract their attention to the matter, and granting access directly to them, if necessary
- Sharing OneDrive content links in Microsoft Teams and controlling user access
- Viewing different file types in OneDrive without having to download the program, e.g., AutoCAD files and 3D images
- Live collaboration on documents and seeing each other’s changes in real-time
- Using check-in/check-out to lock documents for editing during co-authoring, to protect documents from accidental changes or overwriting
- Using versioning to create multiple versions of a document, to prevent duplication of the same document and to enable restoring it to the previous version, if necessary
- Using workflows to streamline and automate processes such as collecting signatures, feedback, or approvals for a plan or a document
- Providing metadata, information about content to classify and categorize it, and to be picked up by the search engine. With SharePoint 2016 a new and improved version of managed metadata was introduced, allowing for even more efficient document classification and discovery.
Protect
Governance in SharePoint Online
If you’re wondering about the exact meaning of the term “governance”, you’re not the only one.
They all boil down to access control – making sure that the right people have access to the right content.
Microsoft 365 Groups is the central tool in collaboration governance. Adding a user to a certain group gives them permission to access its resources. Groups always include collaboration tools such as a SharePoint site, Planner, a Power BI workspace, a mailbox, a calendar, and Stream. There are numerous ways in which users give access, but this one is considered a best practice.
Additional governance capabilities, such as contact sharing restrictions, are available in SharePoint, Teams, and Azure Active Directory. With Azure Blueprints, you can easily implement predefined sets of standards, such as role assignments, policy assignments, resource groups, and resource manager templates. All these services adhere to governance and compliance requirements.
Ensuring proper governance in Microsoft 365 can be a time-consuming process. Luckily, you can automate it.
Syskit Point for Microsoft 365 governance
Imagine controlling user access in a highly regulated industry. Checking permission settings in a variety of different sources, sites, folders, and even files can take hours.
With Syskit Point, it gets done in a couple of clicks.
This Microsoft 365 governance tool is a perfect complement to all the capabilities mentioned above. It tracks user access by providing full transparency in the form of easy-to-understand security reports. In practice, it means that user and admin activity, permissions, and memberships across Microsoft 365 are traceable in a matter of seconds.
As a continuous effort to enforce governance policies, Syskit Point also helps you automate Office 365 governance. It delegates responsibility from the IT team to the site, Microsoft Teams, and Microsoft 365 Groups owners who operationally know who should have which access, and what to do with inactive sites and content. The process is called access review and it is scheduled by periodically sending an automated email request to the site owners who perform it. As a result, you can easily investigate potential Microsoft 365 security breaches and keep your tenant clutter-free.
Security and Compliance in Microsoft 365
Over the past few years, online business owners have equally been losing sleep over cyberattacks and compliance officers. With its many ready-made security and compliance capabilities, Microsoft 365 once again comes to the rescue. Its security best practices can be divided into four main areas:
1. Identity and Access Management
Microsoft identity and access management (IAM) tools enable secure access to resources, fend off suspicious log-in attempts and protect user credentials with the help of risk-based access controls, identity protection tools, and strong authentication options.
2. Threat Protection
With its integrated, automated security solutions, Microsoft threat protection helps secure employee data against emerging cyber threats. Powered by artificial intelligence (AI), Azure Sentinel enables you to detect threats and respond to them quickly. Microsoft 365 Defender and Azure Defender allow you to prevent and detect attacks across your data and cloud apps while protecting your Azure and hybrid cloud workloads.
3. Information Protection
Data Classification enables you to identify important information across your cloud and on-premises environments and add appropriate sensitivity labels to control where the data travels. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) protects your organization’s sensitive information, such as financial data, credit card numbers, health records, social security numbers, etc., by allowing you to create and manage DLP policies in the Microsoft 365 Compliance center.
4. Security & Risk Management
Microsoft 365 security and risk management guards your organization’s critical information by quickly identifying and remediating risks from both malicious and unintentional activities. It encompasses Insider Risk Management, Information Barriers, Customer Lockbox, Privileged Access Management (PAM), and Advanced Audit.
Compliance management in Microsoft 365
With over 220 regulatory updates published every day, the compliance landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Luckily, you don’t have to keep up with all of that – Microsoft Compliance Manager does it for you. Check out its key features:
- Compliance score shows your current standing based on the Microsoft 365 data protection baseline. It allows you to track progress and prioritize actions involving higher potential risk.
- Controls give you a set of actions and procedures required to meet a specific regulation, including system configuration, organizational process, and people responsible for it.
- Assessment includes a grouping of controls that need to be completed to meet the requirements of a standard, regulation, or law.
- Ready-made templates are provided for creating assessments.
- Improvement actions centralize compliance activities.
Microsoft 365 retention policy and retention labels
To retain, or not to retain, that is the question.
By adding retention labels, we decide if and for how long we want to retain different documents.
Retention settings boil down to the following three scenarios:
- Retain-only: Retain content forever or for a specified period.
- Delete-only: Permanently delete content after a specified period.
- Retain and then delete: Retain the content for a specified period and then permanently delete it.
You can assign retention settings to a group of content at a higher level (retention policies), or at an item level (retention labels). For more detailed information about how retention settings work, visit our blog on Microsoft 365 retention policies and labels.
Records and disposition in Microsoft 365 ECM
Records management in Microsoft 365 ECM helps you manage legal obligations, provides the ability to demonstrate compliance, and increases efficiency with regular disposition. Content can be marked as a record or a regulatory record with different restrictions for allowed or blocked actions.
When content is declared a record:
- Restrictions are placed on the items in terms of what actions are allowed or blocked.
- Additional activities about the item are logged.
- You have proof of disposition when the items are deleted at the end of their retention period.
The documents at the end of the retention period can be managed on the Disposition page in the Records Management, but only if you have the Disposition Management role. For more detailed information on permissions and disposition reviews, make sure to read this Microsoft document.
eDiscovery in Microsoft 365
All the different content types residing in the Microsoft 365 ecosystem present potential legal challenges, which is why they need to be easily found. eDiscovery is the process of identifying electronic information that can be used as evidence in legal cases. You can use eDiscovery tools in Microsoft 365 to search for content in Exchange Online, OneDrive for Business, SharePoint Online, Microsoft Teams, Microsoft 365 Groups, and Yammer teams.
Microsoft 365 provides the following eDiscovery features:
- Content search allows you to search for content across Microsoft 365 data sources and export the search results.
- With Core eDiscovery, you can create eDiscovery cases and assign eDiscovery managers to specific cases, associate searches and exports with a case and place an eDiscovery hold on content locations relevant to the case.
- Many features of advanced eDiscovery build on the existing capabilities in Core eDiscovery. Some of them include custodian management, legal hold notifications, advanced indexing, review set filtering, tagging, analytics, predictive code models, and more.
Discover eDiscovery solutions and how they compare to each other.
Harvest
The traditional approach to ECM usually concludes the content management lifecycle with archiving or disposition. This is not the case with Microsoft 365 ECM.
Rather than be forgotten, the archived content should be harvested – reused, audited, researched, edited, measured, and adapted by future users. Thus far, we have reviewed numerous Microsoft 365 ECM tools and capabilities that allow us to do just that. But what about archiving?
Archiving in Exchange Online
In terms of companies’ informational governance strategy, we have previously touched upon retention policies and labels which cover different types of data, including mailboxes, Teams conversations, SharePoint, and OneDrive data. Exchange Online offers further archiving capabilities.
Microsoft 365 archive mailboxes are additional mailbox storage spaces provided to users. After the feature is enabled, it allows for the currently unused data to be moved to a secondary mailbox, relieving the primary mailbox of storage costs.
Each user is initially given 100 GB of storage which can be further expanded after the limit is reached. The auto-expanding archiving is applied automatically, without the need to contact Microsoft (which was previously the case). The auto-expanded archive has a limit of 1.5 TB.
Get informed about enabling auto-expanding archiving.
Final thoughts on the Microsoft ECM
From content creation to harvesting, we have covered a wealth of Microsoft 365 ECM tools and capabilities for all stages of enterprise content management. If you’re eager to take your company’s ECM to the next level, don’t go just yet!
Check out Syskit Point first – it enables Microsoft 365 tools to achieve their full potential. We’ve already mentioned automated governance, security processes, and tracking access control, but its specialty is making IT teams’ lives easier.
And, if you want to learn more about enterprise content management in M365, check out our webinar on the topic:


