How to automate Microsoft Teams governance
Table of contents
Key takeaways:
- Clear governance starts with a simple, well-communicated classification scheme.
- Automation platforms allow for consistent naming conventions, templates, and lifecycle rules to help keep chaos and sprawl at bay as your Teams footprint grows.
- Additional tools enable delegated governance, empowering team owners to handle their responsibilities while reducing IT’s manual workload and ensuring security and compliance stay on track.
- Native tools shine in specific areas, but fragmented portals and reporting gaps make unified oversight tough for large organizations.
Governance can often feel like an endless loop of hopping between portals, toggling settings, and chasing Teams owners who forgot last quarter’s audit checklist. It’s simply not sustainable, and it doesn’t scale either.
Microsoft 365 includes important building blocks for governance, such as Purview sensitivity labels and the compliance center. However, relying on native capabilities alone can introduce limitations, particularly where licensing requirements, manual processes, and consistency across workspaces are concerned. Closing these gaps often requires additional automation layered on top of the platform.
Once a Microsoft Teams governance approach is defined, automation can help translate policy into practice. This includes applying consistent controls during workspace creation, supporting ongoing classification, and enabling governance tasks to be shared responsibly with team owners rather than remaining solely with IT. When implemented thoughtfully, automation reduces operational overhead and helps governance function as a repeatable, sustainable process rather than a series of manual interventions.
Understanding Teams governance automation challenges
Let’s look at a few common scenarios where native tools often require significant manual work or complex scripting to manage effectively:
- Workspace Lifecycle and Archival: What happens when a project-based Team is no longer active? Microsoft 365 does offer native solutions: the Group Expiration Policy to set a lifespan for entire Teams, and Retention Policies to control how long messages and files are kept. However, both tools are inflexible. You can set a single expiration period for Microsoft 365 Groups, but you cannot assign different timelines to different Teams (e.g., 90 days for project Teams vs. 3 years for departmental Teams).
Similarly, retention policies apply broadly and cannot be easily tailored per Team based on its specific business context. Since different Teams serve different purposes and have different lifecycle needs, these one-size-fits-all approaches often fall short, pushing organizations toward more flexible governance solutions. - Ownership Accountability: Microsoft Teams requires at least one owner, but there’s no native mechanism to enforce that owners actively manage their workspaces. An owner might leave the organization, and while Microsoft can auto-promote a member to owner in some cases, there’s no systematic way to ensure that the remaining owners are actually reviewing guest access, checking for compliance, or responding to policy violations. IT ends up manually auditing ownership and sending reminder emails, which is both time-consuming and inconsistent.
- External Sharing and Guest User Reviews: The Microsoft 365 admin center provides visibility into guest users, but it doesn’t offer a streamlined workflow for periodic access reviews at the workspace level. You can see who the guests are, but coordinating a review process where team owners validate whether each guest still needs access requires either manual coordination or building a custom solution using Power Automate and Azure AD access reviews. Even then, tracking responses and ensuring follow-through remains a challenge.
- Reporting and Visibility Gaps: While the Microsoft 365 admin center and Purview provide various reports, getting a consolidated view of governance health, such as which workspaces lack sensitivity labels, which have external users, which are inactive, and which have orphaned ownership, requires pulling data from multiple sources and correlating it manually or through custom scripts.
These gaps highlight why many organizations look beyond native capabilities to dedicated governance platforms that can automate these workflows, provide centralized visibility, and reduce the manual burden on IT teams.
“Admins can lose hours every week to repetitive tasks such as provisioning new teams, chasing unused workspaces, or removing expired guest users. Such approaches simply don’t scale and can often lead to frustrating regulatory issues.”
– Danijel Cizek, Product Manager Team Lead at Syskit
Automating governance delivers four standout benefits:
- Time savings – rules for creation, naming, and lifecycle are applied instantly and uniformly, freeing IT for higher-value work.
- Reduces security gaps by ensuring guest access expires and sensitive data is automatically protected.
- Upgrades compliance, turning audit preparation into a reporting task rather than a weeks-long scramble.
- Brings standardization to every team – from naming conventions to folder structure and permissions – so you get an organized, compliant, and trustworthy Teams environment at scale.
For organizations facing growth, regulation, or tight IT resourcing, comprehensive automated governance that goes beyond native limitations is the difference between a secure Teams ecosystem and an unmanageable admin headache.
Key areas for Teams governance automation
Here are the five main areas where Teams governance automation adds measurable control and consistency across large M365 environments:
- Automated provisioning: Automatically create new teams from predefined templates and approval workflows. Each team starts with the correct structure, membership, and naming conventions, ensuring order even at scale.
- Lifecycle management: Apply a policy to delegate tasks to owners. If an owner ignores a task, automate enforcing automatic deletion or archival. This keeps the tenant clean, improves oversight, and prevents uncontrolled team sprawl.
- Naming conventions: Apply structured naming policies to make teams searchable and standardized across departments.
- Guest and external user management: Conduct regular reviews to minimize risks tied to external collaboration.
- Reporting and auditing: Generate audit-ready reports automatically, giving compliance and IT teams immediate visibility into team activity, ownership, and policy adherence.
For organizations starting their automation journey, focusing first on guest access and lifecycle management often delivers the biggest returns in reducing risk and cleaning up sprawl, while remaining easy to monitor through built-in reporting dashboards.
Teams governance automation with native Microsoft 365 tools

While all tools play a role, this guide will focus on the Microsoft Purview compliance portal and sensitivity labels, as they are a native service for automating the core security and compliance policies that matter most to large organizations.
Microsoft 365 native tools form a layered approach to Teams governance automation, with each having a distinct scope. Understanding where controls actually live helps make automation practical.
Here’s how the control map breaks down:
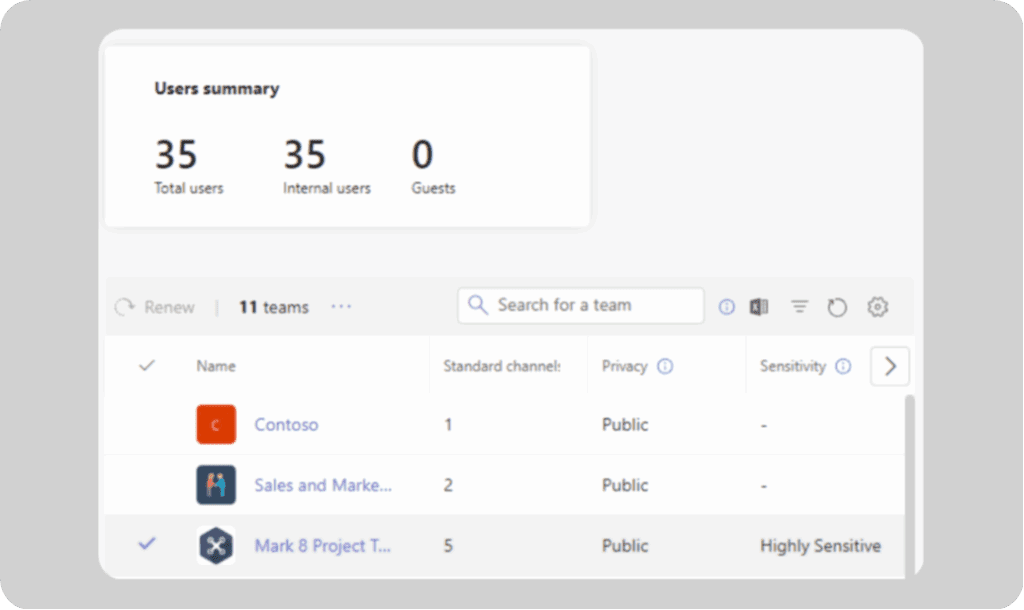
- Teams Admin Center: Configure policies in the Admin Center for client experience, meetings, and messaging.

- Microsoft Entra ID: Handles group creation rights, access reviews, dynamic groups, and sets group expiration policies. Entra ID is useful for regulating who can make teams and ensuring unused ones are cleaned up.
- Microsoft Purview: The compliance control plane. Here, Sensitivity Labels classify teams and automate access restrictions at creation. Retention Policies govern the data lifecycle – keeping or deleting channel content – and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) rules prevent accidental leaks of sensitive information.
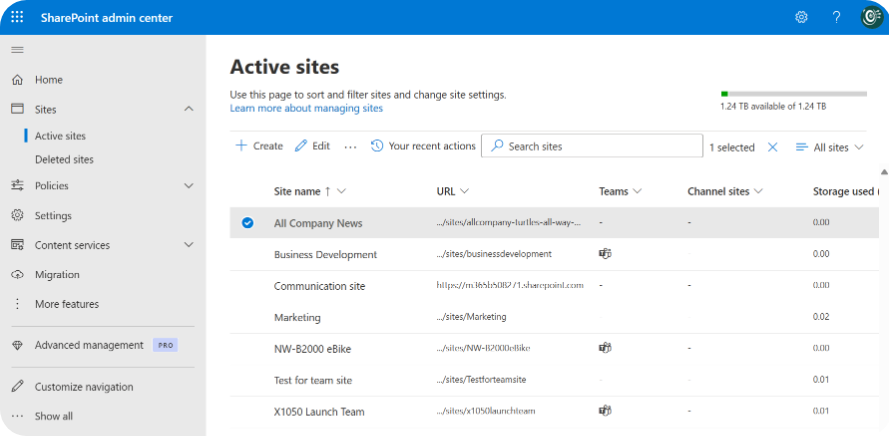
- SharePoint Admin Center: SharePoint controls external sharing at the site level, complementing Purview’s wider protections.
In Microsoft 365, Teams governance can be enforced using native automation tools like Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Entra ID. Use Entra ID to restrict creation and automate reviews, then Purview’s labels and policies for compliance and security at scale.
Together, these capabilities ensure consistent access control, team management, and compliance across the Microsoft 365 environment.
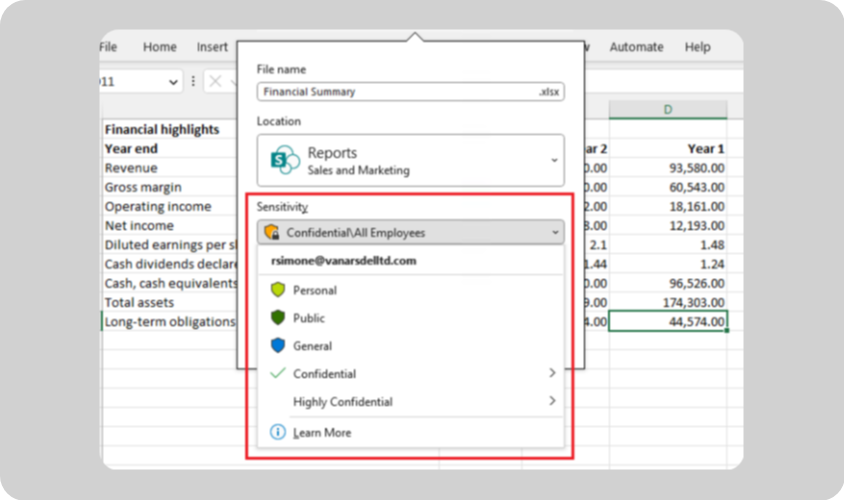
1. Automating Team creation and access with sensitivity labels
Sensitivity labels for Microsoft Teams apply to the container – the Microsoft 365 Group behind each team. This means that instead of labeling individual files, the label governs how the team behaves – who can access it, whether guests are allowed, and how it’s classified.
Step 1: Define your classification scheme
Start with a simple, clear structure that users can understand, like General, Confidential, and Highly Confidential. Each category should directly translate to access rules that make sense for your organization’s data types.
Step 2: Create the labels in Microsoft Purview
Head to the Microsoft Purview compliance portal, then Solutions > Information Protection > Sensitivity Labels > Create a Label. Define the name, description for users, and scope as Groups & Sites, ensuring the label applies to Teams and Groups.
Step 3: Configure the automation settings
Within the Groups & Sites section, configure:
- Privacy: Set whether the team should be Public or Private by default.
- External User Access: Automatically allow or block guest access. This control can prevent data exposure and is one of the most impactful security toggles available.
Step 4: Publish the label policy
In Purview > Information Protection > Label Policies, choose Publish Labels and assign which users or groups can apply them. Once published, users creating a new team will see a mandatory dropdown – General, Confidential, etc – and their selection will automatically configure the team’s privacy and guest settings.
Building a lightweight approval workflow
To control new team requests, pair sensitivity labels with a Power Automate approval flow. Such a workflow would resemble the following:
- Requires a request form to capture metadata like team purpose and owners.
- Applies naming conventions and ensures required owners are filled in.
- Triggers an approval from IT or a department head.
- Upon approval, automatically creates the team with the correct sensitivity label, ensuring compliance and consistency from day one.
2. Automating data lifecycle and compliance in Purview
Automating data retention
Retention policies in Microsoft Purview help organizations control how long Teams data lives, ensuring old content doesn’t linger or vanish prematurely. The goal is to align with internal and regulatory rules, like deleting all chat messages after 90 days or retaining financial records for seven years.
To configure this, sign in to the Microsoft Purview compliance portal, then hit Solutions > Data Lifecycle Management > Policies > Retention Policies. Select New retention policy, name it, and choose whether it’s Static or Adaptive.
Next, assign it to Teams channel messages and Teams chats, select a retention duration, and choose an action – retain-only, delete-only, or retain-then-delete. Once published, Purview automatically applies these rules across all scoped Teams data, continuously maintaining compliance without manual cleanup.
Automating data protection with DLP
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies automatically detect and block sensitive data from being shared, reducing accidental exposure.
Automate this in Purview via Data Loss Prevention > Policies > Create Policy, then choose a template (e.g. Financial Data, Privacy, or Custom). Assign it to Microsoft Teams Locations, enable detection for sensitive information types such as credit card numbers or national IDs, and configure what action to take – warn, block, or report.
“This enforcement happens automatically, often within seconds, so protected data never leaves approved boundaries. Together, retention and DLP policies form the core of automated compliance for Microsoft Teams, keeping data under your control every day.”
– Danijel Cizek, Product Manager Team Lead at Syskit
The coordination problem: Managing policies across multiple admin centers
Even with Microsoft 365’s native toolset, managing governance at scale quickly hits a wall, as every automation lives in a different admin portal.
If you need to review access or check lifecycle status for a team, you’ll find policies scattered across the Teams Admin Center, Microsoft Entra ID, Microsoft Purview, and even SharePoint Admin Center, with each handling just a piece of the wider puzzle.
This fragmentation creates the portal-hopping problem. Admins must jump between centers to set, review, or audit policies, with no central dashboard to manage all rules in one place. When overseeing hundreds of teams, this leads to missed reviews, overlooked lifecycle policies, and inconsistent enforcement.
Creating compliant, audit-ready environments demands expertise, but still leaves gaps. Native tools simply can’t automate access reviews or ownership attestations end-to-end without resorting to advanced PowerShell scripting or extra manual steps. Many teams struggle to prove which retention, sensitivity, and expiration policies are applied to each workspace.
The result is that reporting is siloed, making it tough to answer auditors or execs with a single, unified view. Audit preparation becomes a time sink and increases the risk of policy drift across fast-growing Teams environments.
Unifying your automation policies with Syskit Point
Syskit Point acts as an orchestration layer above native SharePoint, OneDrive, M365 Groups, Power Platform, and Teams, allowing you to manage these within a single, logical dashboard. This consolidation means admins can finally control complex environments from a single location, eliminating the headache of portal-hopping and fragmented oversight.
With Syskit Point, you don’t need deep expertise in Purview, Entra, or PowerShell. The platform’s visual interface makes it straightforward to create and enforce governance policies, regardless of where the underlying controls originate. Configuring policies, reviews, and approval workflows is fast and does not require any code.
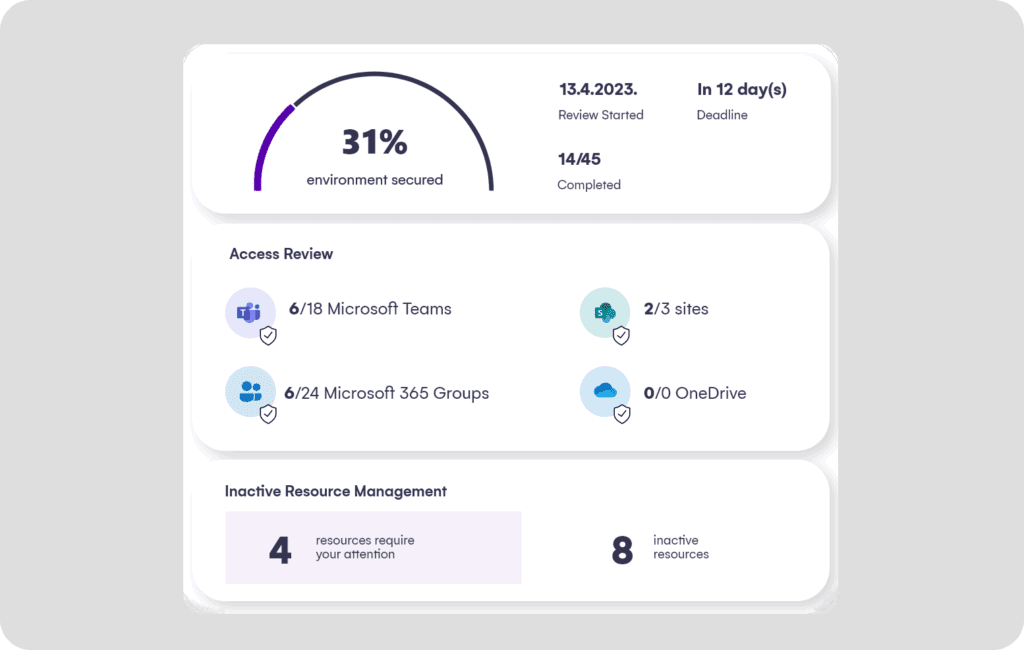
Out of the box, Syskit Point delivers automation for workspace reviews, ownership attestation, and orphaned team cleanup. These functions are highly difficult to implement natively, or require time-consuming scripting. Scheduled reviews and proactive alerts keep security and compliance automatically on track.
Syskit Point leverages native sensitivity labels as persistent triggers for lifecycle management. For example, if a team is labeled Highly Confidential, Syskit Point can continuously enforce controls like requiring three owners and setting up quarterly access reviews. With our platform in your tech stack, compliance is entirely possible from creation to deletion.
“Instead of chasing reports across different admin centers, Syskit Point generates detailed, audit-ready reports that show all applied policies and permissions for any team at the click of a button. This slashes audit prep time and provides assurance for stakeholders and regulators.”
– Danijel Cizek, Product Manager Team Lead at Syskit
Syskit Point offers further functionality through its integrated Microsoft Teams App, giving employees the ability to request new workspaces, handle approvals, and engage with governance processes directly inside the Teams environment.
While the main Syskit Point solution delivers unified, automated governance, in-depth reporting, and policy enforcement for administrators, the Teams App improves usability for everyday users – enabling broader adoption by making workspace requests and provisioning simpler and more widely distributed.
How to measure your governance impact
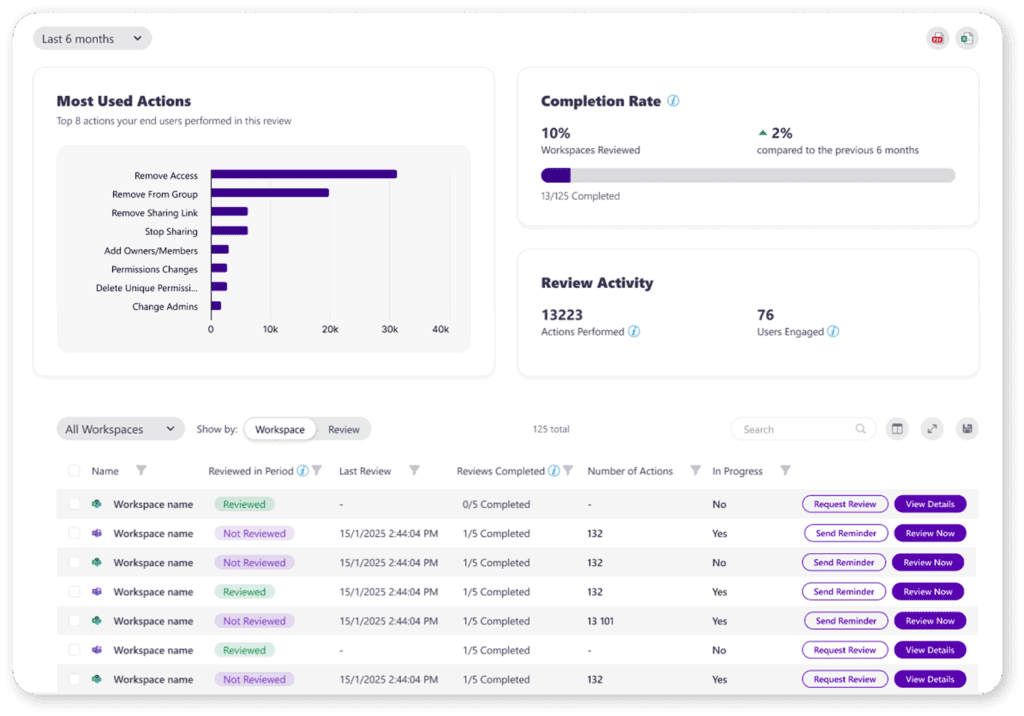
This is where Syskit Point’s Insights Dashboard comes in. It translates your automated governance efforts into a clear story of risk reduction, providing the concrete metrics needed to demonstrate the true ROI of your strategy to stakeholders. The dashboard offers a transparent view into all automated actions, from the removal of a specific inactive guest during an access review to the cleanup of an expired “anyone” link.
By aggregating these granular, action-oriented metrics, you can move beyond simply managing the environment to proving its health. The dashboard allows you to build a high-level narrative, confidently showing leadership the tangible reduction in security risks and compliance gaps across your Microsoft 365 environment over time.
Activate your automated Teams governance framework
Sustainable, effective Teams governance scales only when you move beyond reactive manual controls and use a central platform to connect, automate, and monitor the native tools already in your stack.
Pairing Microsoft automation with Syskit Point makes this shift possible. Instead of juggling compliance tasks across portals, teams get proactive, policy-driven, and audit-ready automation by design. Syskit Point acts as the control tower – executing, reporting on, and enforcing policy everywhere from a single place.
That’s how enterprises like The Rimac Group (owner of Bugatti) keep their Teams environment secure at speed and scale.
“We’re Teams addicts, and the Syskit Point Teams application feels native to us. It provided a familiar interface for our end-users to request new workspaces without leaving MS Teams… Tracking user and admin actions helped us have control over suspicious activities.”
– Robert Preskar, Head of IT Projects, Rimac Group
If you’re looking to move from fragmented tools to a governance system that’s proactive, nimble, and fully secure, try Syskit Point today.


